Cutting Fluids Types and Applications
Cutting fluids, also known as coolant or lubricant, play a crucial role in various machining processes. The common use of cutting fluid is to cool and lubricate the cutting tool and workpiece during operations. They play a crucial role in manufacturing processes. Such as functioning to cool, lubricate, and clean the cutting tool and the workpiece surface. The right cutting fluid can enhance machining performance, minimize tool wear, and increase process efficiency. With several cutting-fluid types including synthetic fluid, emulsions, semi-synthetic fluid, and straight oils. Materials engineers and machinists can choose the ideal fluid to meet specific machining demands.
This article provides valuable insights into the types and applications of those fluids. This article helps you to select the industry’s best cutting fluids for your manufacturing processes.
What is Cutting Fluid
Cutting fluids are compounds that are used to lubricate and cool the cutting surfaces and workpieces during the machining process. They are utilized in machining processes such as drilling, grinding, and cutting. Primarily these fluids will improve the accuracy of machining, increase tool life, and reduce heat generation. To reduce the heat generation it will reduce the friction between the cutting surfaces and the workpiece.
Cutting fluids come in different forms like synthetic, semi-synthetic, soluble, and straight oils. Each of these is designed to provide unique properties that meet specific machining demands. These fluids play a crucial role in modern manufacturing. They are allowing industries to produce stronger, more efficient, and more precise components that meet or exceed customer expectations.
Where use the Cutting Fluids
Industries utilize cutting fluids in various machining operations to enhance cutting performance. Compare to conventional machining processes modern and CNC machining processes are like to have coolants. Following are the typical machining operation where cutting fluids are used.
- Turning
- Milling
- Drilling
- Grinding
- Sawing
- Tapping
- Boring
- Plasma cutting
Some common Engineering Materials require different cutting fluids depending on material types. For example, aluminum and stainless steel materials require different fluids.
Function and Benefits of Cutting Fluid
Cutting fluids provides several benefits that significantly impact machining operations. They effectively dissipate heat generated during cutting, preventing thermal damage and maintaining dimensional accuracy. Through lubrication, cutting fluids minimize friction and wear, resulting in improved surface finish and prolonged tool life. The use of cutting fluids enhances chip evacuation, improving material removal efficiency, and reducing the risk of chip-related issues.
Moreover, these fluids provide corrosion protection, safeguarding both the workpiece and cutting tools. Cutting fluid plays a vital role in optimizing productivity and achieving high-quality results in machining processes.
Followings are some of the benefits of cutting fluids.
- Cooling
- Lubrication
- Chip Evacuation
- Corrosion Protection
- Surface Finish Improvement
- Extended Tool Life
- Improved Machining Efficiency
Properties of Cutting Fluids
There are different types of cutting fluids and cutting fluid properties. When you are selecting a cutting fluid you need to think about the following factors.
- Viscosity
- Thermal Stability
- Lubricity
- Cooling Capacity
- Chemical Compatibility
- Corrosion Resistance
- Foam Control
- Environmental Impact
- Odor
- Health and Safety
Types of Cutting Fluids
There are different types of cutting fluids such as Straight Oils, Soluble Oils, Synthetic Fluids, and Semi-Synthetic Fluids. The following chat shows the industry cutting fluid usage.
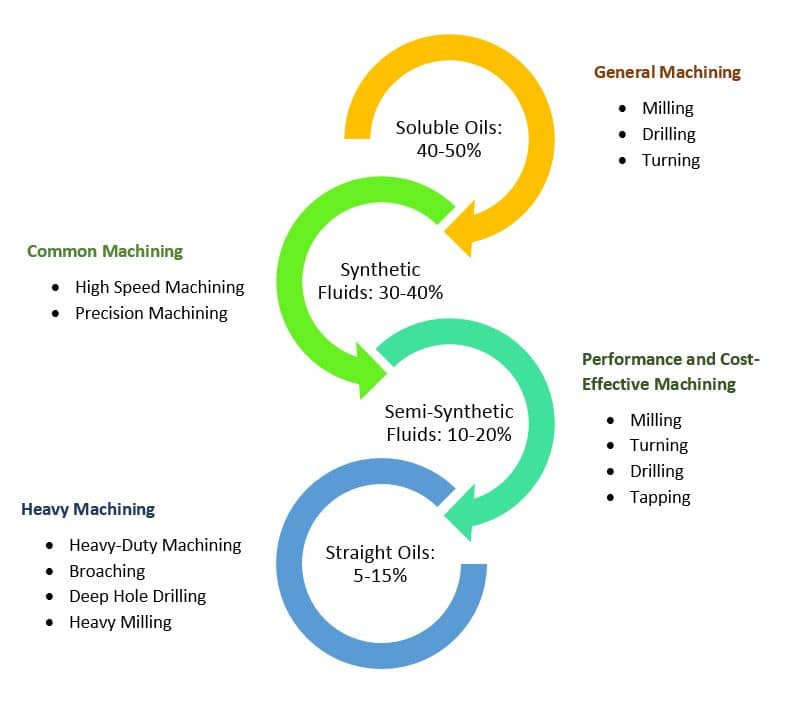
Straight Oils
Straight oils, also known as neat cutting oils, are used as cutting fluids in machining processes. Composed of mineral or vegetable-based oils, these fluids provide lubrication and reduce friction between the cutting tool and workpiece.
Straight oils are particularly suitable for heavy-duty machining operations that involve high cutting forces. They offer excellent stability, low foaming, and compatibility with a wide range of materials.

However, they have limited cooling capabilities compared to water-based fluids and may require additional cleaning steps after use. Despite these limitations, straight oils are favored for their lubrication properties and are commonly employed in various machining applications.
Soluble Oils
In machining processes, industries widely use soluble oils, also known as emulsifiable oils, as cutting fluids. These fluids consist of a mixture of mineral or synthetic oils and emulsifiers, allowing them to mix with water.
Soluble oils offer several advantages,
- It has excellent cooling and lubrication properties.
- It can dissipate heat effectively
- Reducing tool wear and improving surface finish.
Additionally, they provide good rust and corrosion protection for the workpiece and tool. Soluble oils are versatile and can be used in various machining operations. These are suitable for a wide range of materials.
However, they require careful monitoring of concentration and regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Synthetic Fluids
Synthetic fluid is a type of cutting fluid widely used in machining processes. Manufacturers formulate these fluids with synthetic base oils and a variety of additives to deliver superior performance.
Synthetic fluids offer numerous advantages,
- Excellent cooling and lubricating properties.
- High thermal stability
- Good for high-temperature operations.
- It will extend the tool’s life.
Synthetic fluids also exhibit low foaming tendencies, ensuring consistent cutting performance. They are compatible with a wide range of materials and offer improved corrosion protection.
Furthermore, synthetic fluids are known for their long fluid life and reduced environmental impact. Their enhanced performance and versatility make them a popular choice for demanding machining applications.
Semi-Synthetic Fluids
Semi-synthetic fluid is a type of cutting fluid that combines the benefits of synthetic and soluble oils. These fluids contain a mixture of synthetic base oils and water, along with additives.
They offer improved cooling and lubrication properties compared to soluble oils while maintaining good compatibility and cost-effectiveness.
Factors to Consider when Choosing Cutting Fluids
When choosing cutting fluid, individuals should consider several factors. These include the specific machining operation they are performing, the type of workpiece material, and cutting conditions such as speed and depth of cut. The environmental impact of the fluid, and the health and safety implications associated with its use.
- Machining Operation: Different operations may require specific fluid properties.
- Workpiece Material: Certain fluids are more compatible with specific materials.
- Cutting Conditions: Consider factors like cutting speed, feed rate, and depth of cut.
- Environmental Impact: Assess the fluid’s eco-friendliness and disposal requirements.
- Health and Safety: Evaluate any potential hazards or risks associated with the fluid.
- Cost-effectiveness: Consider the fluid’s price, lifespan, and maintenance requirements.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure the fluid meets relevant industry regulations and standards.
Thank you for reading our cutting fluids article. We hope the information provided helps you understand the importance of selecting the right cutting fluid. In upcoming articles, we will discuss more details about cutting fluid. If you have any questions, feel free to reach out. Happy machining!
0 Comments